Mekong Sustainable Manufacturing Alliance (The Alliance)
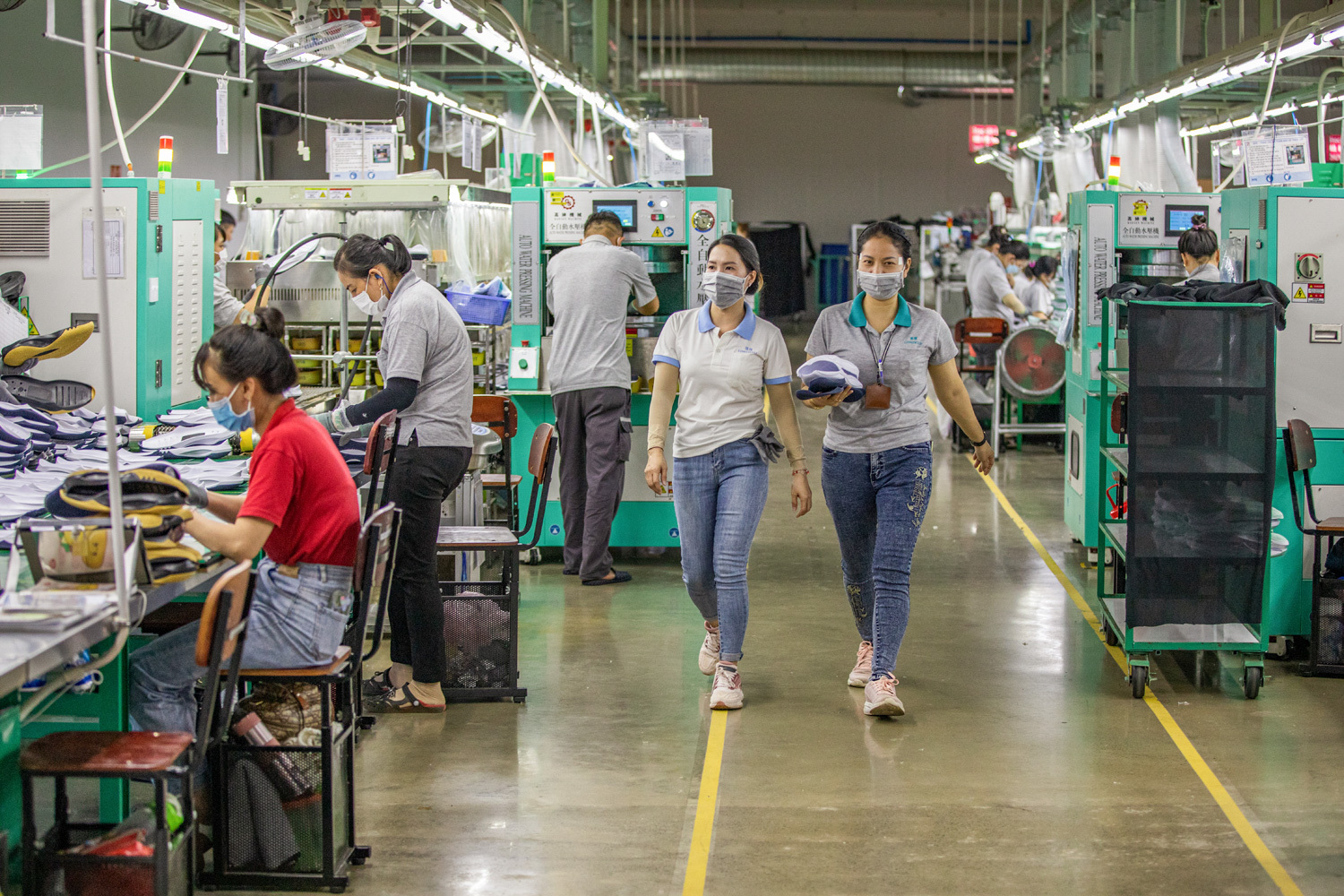
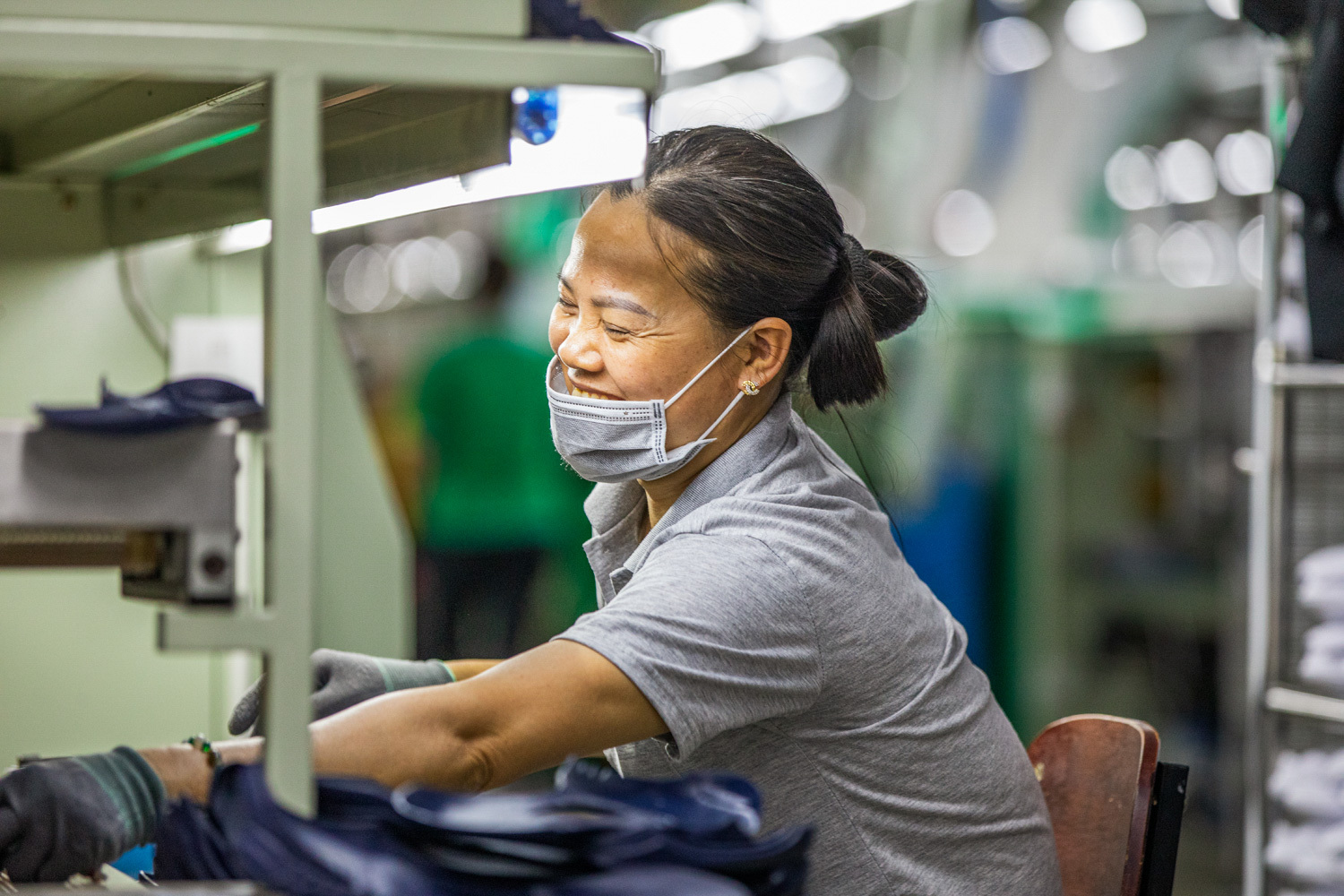
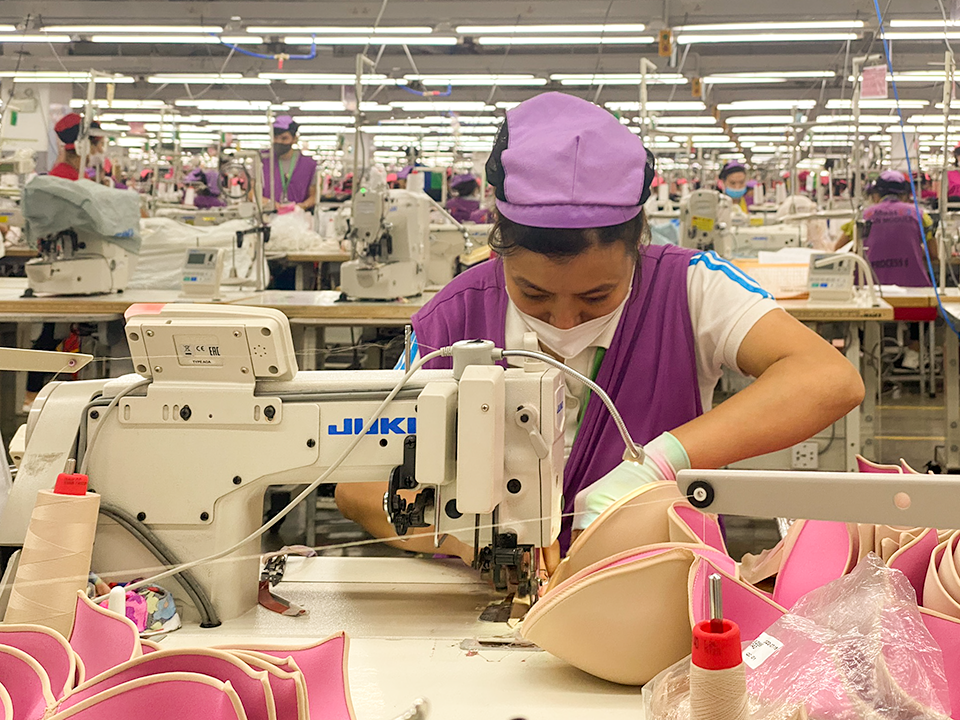
In 2020, ISC established the Mekong Sustainable Manufacturing Alliance (The Alliance) in partnership with ELEVATE and the Asian Institute for Technology with funding from the United States Agency for International Development (USAID). The Alliance partners with local factories, while engaging multinational brands, to support the implementation of Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) standards in the Mekong’s multi-sector manufacturing region.
Why Adopt ESG Standards?
Factories in the Mekong region are at a crossroads. Business owners face a choice between adopting ESG standards that will increase sustainability and make them more competitive in the international market or employing lower-cost, but ultimately, counterproductive practices that compromise natural resources, the health and safety of factory workers, and the well-being of surrounding communities.
ESG interventions generate a positive return on investment (ROI) by enabling manufacturers to meet global buyers’ sourcing standards, lowering operating costs, and/or increasing productivity. The manufacturing sector has tremendous potential to set the region on a sustainable development path if obstacles blocking manufacturers’ adoption of ESG standards can be removed. These obstacles include manufacturers’ limited awareness and understanding of the positive ROI that ESG investments generate, their lack of knowledge and skills required to execute ESG improvements, and their inability to access ESG financing.
How We Work
The Alliance employs a multi-pronged strategy to engage directly with local factories in Cambodia, Thailand, and Vietnam with the goal of creating a larger ecosystem of manufacturers that support continuous improvement and sustainability.

Our multi-pronged approach includes:
- Tailored technical assistance in implementing decarbonization solutions to help reduce GHG emissions, and driving improvement in gender, social and governance solutions
- Capacity-building projects broaden factory management’s knowledge in energy efficiency, renewable energy, and in creating a respectful workplace
- Facilitating regional dialogues, industry-level exchanges of best practices and collaborative actions on ESG-related topics, including but not limited to decarbonization solutions, and sustainable finance.
This powerful, multi-pronged approach catalyzes market-driven choices by factories to improve their ESG standards. It enables manufacturers, in coordination with the global brands they supply, to adopt climate-smart and socially-compliant technologies and practices that result in greener and safer production. Moreover, it demonstrates to factories that environment, health, and safety improvements can go hand-in-hand with improved competitiveness and profitability, thus fostering the region’s economic growth and supporting its journey to self-reliance.
Sustainable Biomass Guidelines
The fashion industry represents an important contributor to the global energy use and greenhouse gases (GHG) emissions. Due to lengthy supply chains and energy-intensive production methods, the fashion industry generated approximately 2% of global carbon emissions (based on data from 2019 from Global Carbon Emissions of Apparel Sector). Without mitigation solutions, emissions from production are set to rise 60% by 2030, up to an estimated 1.6 billion tons of carbon.
Biomass plays an important role in terms of primary energy supply particularly in the developing and under development countries. Due to the carbon captured during its lifecycle, biomass can be considered as a low carbon transition energy source to produce hot water and steam generation, in substitution of fossil fuels required in system processes, such as textile production and the manufacturing of clothes. Nevertheless, while representing an alternative solution for phasing out of fossil fuels, biomass production, transportation and utilization can also generate direct and indirect negative environmental and social impacts such as deforestation, air pollution from biomass combustion or competing use between food and energy purposes. Therefore, defining and assessing the sustainability of biomass sources needs to be done properly along the supply-chain.
These guidelines have therefore been prepared with the objectives to:
- Gain understanding on the different types of biomass and the environmental and social risks that may occur through the supply chain.
- Support key decision-makers in selecting biomass types that are acceptable or can be acceptable with certain risk mitigation action plans and in screening biomass suppliers providing the necessary references and tools related to E&S risks screening analysis.